Both FSSAI and FSI fall under the supervision of the Government of India and operate with the identical primary objective of safeguarding the safety and security of food, In this article, we explained the importance and difference between FSSAI and FCI.
What is FSSAI?
The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, the government of India, regulates the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), a self-sustaining organisation. It is an independent corporation founded by the Indian government’s Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, a streamlined law dealing with food safety and regulation in India, is the legislation that led to the formation of the FSSAI. The regulation and oversight of food safety is an obligation of the FSSAI to safeguard and promote public health.
Objectives of FSSAI
- Its primary objectives are to guarantee food safety and serve as an organisation that legally certifies businesses engaged in food production and processing.
- The FSSAI is authorised to establish several rules and regulations that are based on science and put the needs of individuals first when it comes to food safety.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is empowered to develop strict standards for all food business operators to manufacture foodstuff while taking into account food quality and sanitary conditions, correct storage and distribution, and regulation of sales and import of the food, all of which needs to be done following the regulations.
- It is in charge of developing knowledge of national requirements for food security and safety.
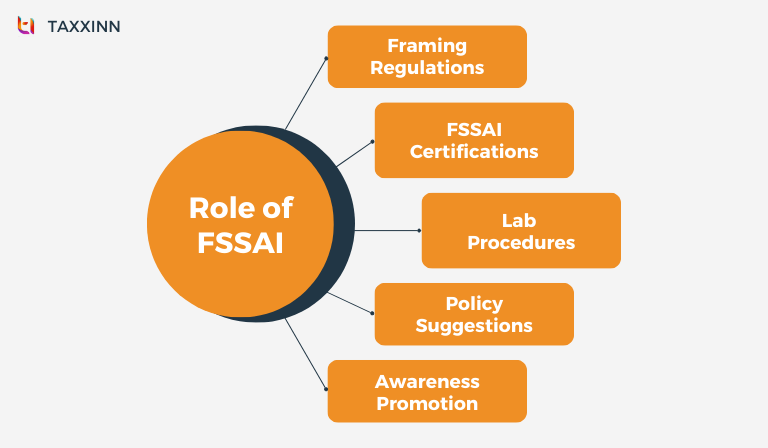
Role Of FSSAI
The FSSAI plays a pivotal role in ensuring food safety and regulating food-related matters in India. Its primary responsibilities include:
- Establishing standards and guidelines for food safety.
- Granting FSSAI food safety licences to food businesses.
- Setting guidelines for laboratories in food businesses.
- Providing input to government policies.
- Gathering data on contaminants, emerging risks, and a rapid alert system.
- Creating a nationwide food safety information network.
- Promoting general awareness about food safety and standards.
What is FCI?
The Food Corporation of India (FCI) is an organisation that the Indian government established. As a result of the Food Corporation Act, of 1964, which was enacted by the Indian Parliament, the food corporation is an officially recognised organisation that comes within the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution. The Food Corporation of India, which holds the Chairman title for its most senior executive, acquires rice and wheat from farmers through a variety of pathways, including paddy purchase centres, mill levies, and custom milling, and subsequently maintains them in warehouses. FCI operates an array of storage facilities, including food storage depots, buffer storage complexes, and private equity godowns. It has additionally adopted the most up-to-date storage techniques for underground storage facilities.
Objectives Of FCI
- FCI strives to be certain that there is an adequate supply of food. It emerged as a reaction to the Green Revolution’s objective of establishing self-sufficiency in rice and wheat.
- To protect the interests of farmers, the Food Corporation of India intends to carry out effective price support operations.
- To perform duties for the public distribution system and transport food products throughout the nation.
- To safeguard sufficient supplies of food grains to guarantee national food security.
- FCI plays an essential role in the change of the food security programme beyond one that is crisis management driven to a steady programme. Some of them are:
- Offer farmers adequate compensation.
- For the benefit of particularly disadvantaged members of society as a whole, keep food grains affordable.
- To determine food security, preserve buffer stocks of food.
- To take action in markets to stabilise prices.
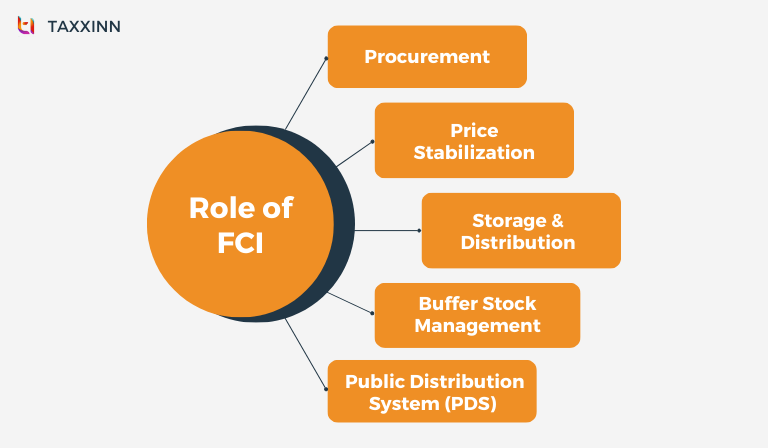
Role Of FCI
The Food Corporation of India (FCI) plays a vital role in India’s food security and distribution system. Its primary responsibilities include:
- FCI procures food grains, such as rice and wheat, from farmers to ensure fair prices and support agricultural stability.
- It maintains a vast network of storage facilities to store the procured food grains safely and hygienically, preventing spoilage and wastage.
- FCI is responsible for the distribution of food grains to various states and union territories, ensuring a consistent and equitable supply across the nation.
- FCI manages buffer stocks of food grains to stabilize prices, meet emergency requirements, and prevent shortages during times of crisis.
- The organization operates the PDS, which provides subsidized food grains to eligible beneficiaries, including the economically disadvantaged, to ensure food security for all.
- FCI plays a crucial role in stabilizing food prices by managing supply and demand, thus preventing sudden spikes or shortages.
Difference Between FSSAI and FCI
| FSSAI | FCI |
| By certifying enterprises that manufacture and prepare food, the FSSAI protects food safety. | Implementing efficient support operations, FCI secures the security of Indian farmers. |
| FSSAI strives to boost public understanding about standards for food security, hygiene, and safety. | FCI has an important competitor in the market and wants to keep pricing stable. |
| Food safety and high quality are the primary objectives of FSSAI. | FCI’s primary objective is to offer high-quality food grains. |
| To enhance consumer food safety, the FSSAI has been authorised to adopt an array of guidelines and suggestions based on science. | An essential role is performed by the Food Corporation of India towards the evolution of short-term food security into a long-term security strategy. |
| It functions under the control of the Indian government’s Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. | It functions underneath the Indian government’s Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution. |
Conclusion
The FSSAI and FCI have significant contributions towards the Indian food environment, but their roles, responsibilities, and missions vary significantly from one another. The major difference between FSSAI and FCI is that FCI maintains food security and price stability through the purchase, storage, and distribution of vital food grains, while FSSAI promotes public health by maintaining standards for food safety and quality throughout a broad variety of food products. To efficiently provide and regulate India’s food business and guarantee the well-being of its population, one must understand those differences. So obtaining an FSSAI licence is necessary for all food business owners to comply with government rules. At Taxxinn, we help to get the FSSAI licence with ease at a reasonable price.
Related Reads,
Difference Between FSSAI Registration and Licence.
FSSAI Registration – A Detailed Guide.